Aggregates, filler and binder in bituminous pavement
In bituminous materials, course aggregates perform the bulking action of the mixture and contributes to the stability of resulting mix. Fine aggregates form the major proportion of mortar.
Filler: it stiffens and strengthens the binder.
Binder: cements the whole mixture together and provides waterproofing.
Asphalt mix design – durability vs stability
The main objective of asphalt mix design is to achieve a mix with economical blending of aggregates with asphalt to achieve the following:
(i) Workability to facilitate easy placement of bituminous materials without experiencing segregation;
(ii) sufficient stability so that under traffic loads the pavement will not undergo distortion and displacement;
(iii)durability by having sufficient asphalt;
(iv) sufficient air voids
In asphalt mix design, high durability is usually obtained at the expense of low stability. Hence, a balance has to be stricken between the durability and stability requirements.
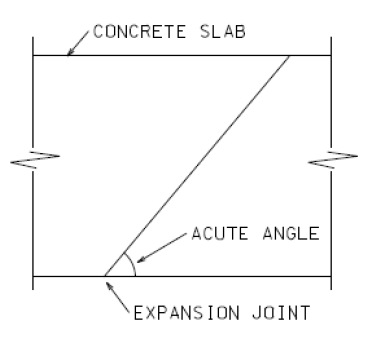
Avoidance of designing acute angle of concrete pavement
The stress induced in acute angle corners of concrete pavement is far much higher than that in right-angle corners of the pavement. For instance, concrete pavement corner of acute angle of 70 degree induces stresses about 50% more than the stress induced by an angle of 90 degree. As a result, corners of concrete pavement should not be designed with cute angles to avoid corner cracking. If it is necessary to adopt acute angles for concrete pavement, special reinforcement has to be provided to strengthen these corners.
Bitumen emulsions – difference between anionic emulsions and cationic emulsions
Bitumen emulsions consist of particles of bitumen dispersed in water by using emulsifying agent. When the emulsion breaks, it represents a change from a liquid to a coherent film with bitumen particles coagulating together. The sign of breaking is the change of colour from brown to black as the colour of emulsion and bitumen is brown and black respectively.
There are in common two broad types of emulsions, namely anionic emulsions and cationic emulsions. The breaking of anionic emulsions is dependent on the evaporation of water from bitumen emulsion. As such, it poses difficulty in wet weather condition. However, for cationic emulsions, instead of relying on the evaporation of water the breaking is achieved by chemical coagulation. Hence, cationic emulsions are particularly useful in wet weather conditions.
No comments:
Post a Comment