It is the instrument used to estimate the dust or suspended particulate matter present in the gaseous state. It works on the principle of centrifugal force. A cyclone collector consists of a cylindrical shell, conical vase, dust hopper and an inlet where the dust laden gas enters tangentially. Under the influence of the centrifugal force generated by the spinning gas, the solid particles are thrown to the walls of the cyclone as the gas spirals upward at the inside of the cone. The particles slide down the walls of the cone and into the hopper.
The operating or separating efficiency of a cyclone collector depends on the magnitude of the centrifugal force exerted on the particles. The greater the centrifugal force, the greater the separating efficiency. The magnitude of the centrifugal force depends on the particle mass, gas velocity within the cyclone collector and the cyclone diameter.
The centrifugal force on the particles and the efficiency of the cyclone collector can be increased by decreasing the radius of the cyclone (R). Large diameter cyclones have good efficiency for the particles 40-50 μm in diameter. High efficiency cyclone with diameter of 23cm (9inch) or less have good efficiency for particles from 15-20μm.
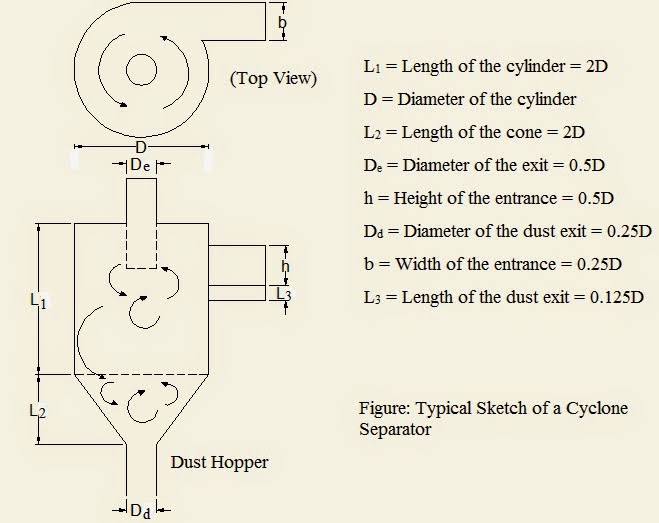
Multiple cyclones operating in parallel are necessary to treat large flow when a small diameter cyclones are used. The cleaning efficiency for such type of units may be as high as 90% for particulates in the 5-10μm range. The smaller radius of the cones not only increase the centrifugal force but also reduce the distance the particles have to travel to reach the collection chamber. A small cyclones do have some disadvantage such as problems with equalizing gas flow to each cone. Abrasion of tubes due to high velocity and plugging of heavily loaded tubes. Cyclones are usually built to standard relative dimensions as shown in the figure above.

Great blog! The explanation of how Cyclone Separator function and their role in enhancing system efficiency was clear and informative. It's impressive how these devices offer a low-maintenance solution for separating particulates in demanding industrial settings. Looking forward to more insightful posts like this!
ReplyDeleteI prefer this response